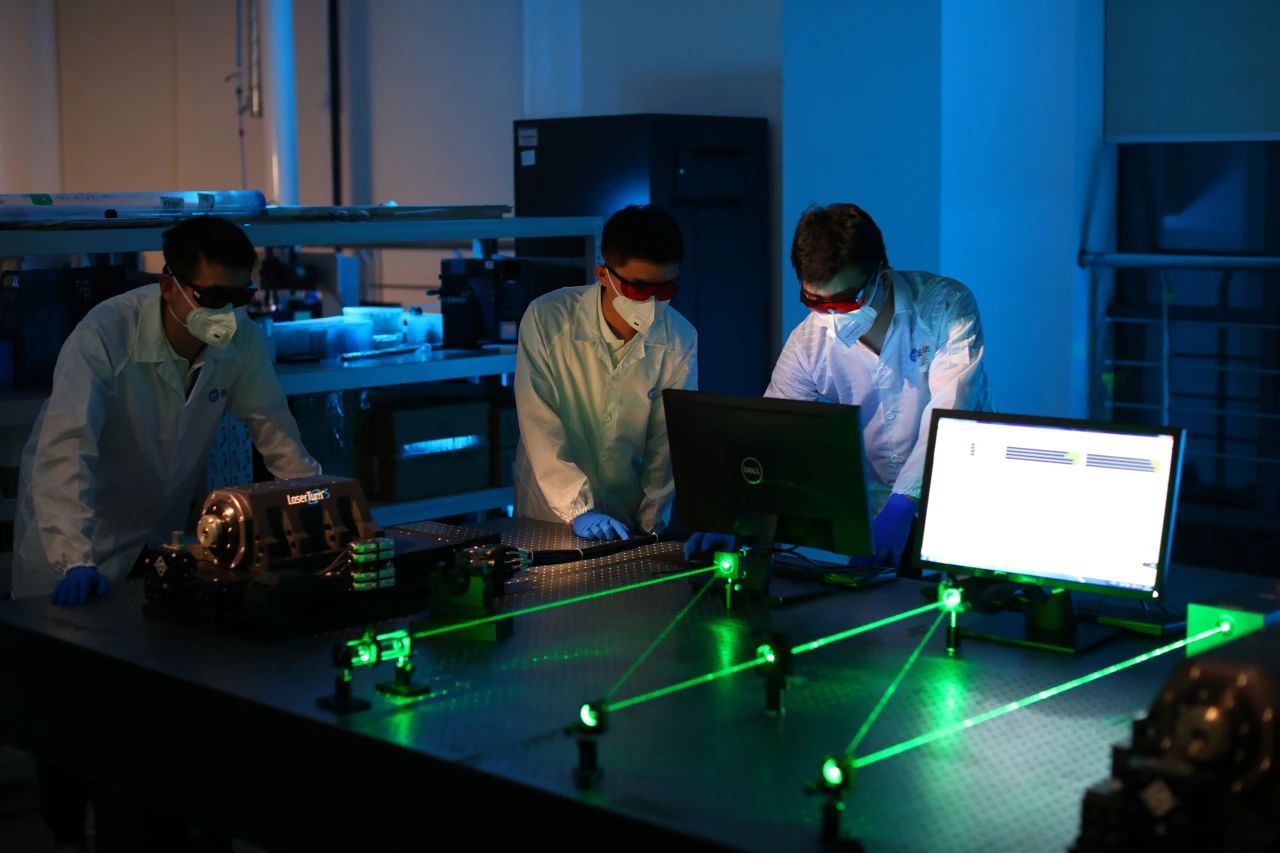
When people hear the word "radiation," they often associate it with danger. However, electromagnetic radiation is ubiquitous in our daily lives and work environments. Laser radiation, as a type of electromagnetic radiation, is not harmful to the human body when used correctly and with appropriate safety measures. This article explores the classification of radiation and the characteristics of electromagnetic radiation.
1、What is radiation?
Radiation refers to the phenomenon of energy propagating through space in the form of electromagnetic waves or high-speed particles. In nature, any object with a temperature above absolute zero (-273°C) emits radiation. Although radiation is ubiquitous, not all forms of it are harmful to humans. Based on its form, radiation can be classified into two categories: electromagnetic radiation and particle radiation.
Electromagnetic radiation spans a wide range of frequencies, from radio waves, microwaves, and infrared rays to visible light, X-rays, and gamma rays. Particle radiation, on the other hand, consists of high-speed particle streams, such as electrons, protons, neutrons, alpha particles, and beta particles.
![News pictures 1]()
2、What is electromagnetic radiation?
Electromagnetic radiation encompasses all radiation that propagates in the form of electromagnetic waves, ranging from radio waves, microwaves, and infrared rays encountered in daily life to high-energy electromagnetic waves such as X-rays and gamma rays used in medical and industrial applications.
Based on the energy levels of electromagnetic radiation, it can be further classified into two types:
Non-ionizing radiation: This type has lower energy and cannot ionize matter. Examples include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, and visible light. Non-ionizing radiation is commonly produced by everyday devices like mobile phones, microwave ovens, and televisions.
Ionizing radiation: This type has higher energy and can ionize atoms or molecules, potentially causing damage to matter. Typical examples are X-rays and gamma rays, widely used in medical imaging and radiation therapy.
Both types of radiation have different applications and effects, with non-ionizing radiation being generally safer for everyday use, while ionizing radiation requires proper safety measures due to its potential risks.
![News pictures-3]()
3、Laser radiation belongs to non-ionizing radiation
It is a unique form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths that can span the infrared, visible light, or ultraviolet range. Since lasers typically fall within the non-ionizing spectrum, they do not cause ionization damage to the human body like X-rays or gamma rays.
What makes laser radiation special is its high energy density and monochromaticity (single wavelength). Although its energy is highly concentrated, the risks associated with laser radiation are manageable as long as precautions are taken to prevent direct or reflected beams from contacting the eyes or skin. This controllability makes lasers safe for use in a wide range of applications across industries.
![News pictures 2]()
In summary:
Electromagnetic radiation is present everywhere in our daily lives and work environments. As a type of non-ionizing radiation, laser radiation poses no harm to the human body when used correctly and with proper protective measures.